Table of Contents
Email Connectors
 Updated
by Niamh Ferns
Updated
by Niamh Ferns
Email Connector Overview
The email connector is a key feature in the Tokity Service Ticketing System that helps automate your support process by retrieving emails and turning them into service tickets or ticket comments. With this feature, customer emails sent to your support address are efficiently managed and never missed.
support@yourdomain.com or help@yourdomain.com. This dedicated email will be used for support communications.Registering a Microsoft User Account
To connect your support email account to Tokity, follow these steps:
- Log in to the Tokity Admin Portal and head to
Email Connector>Receiver Accounts - Click Register
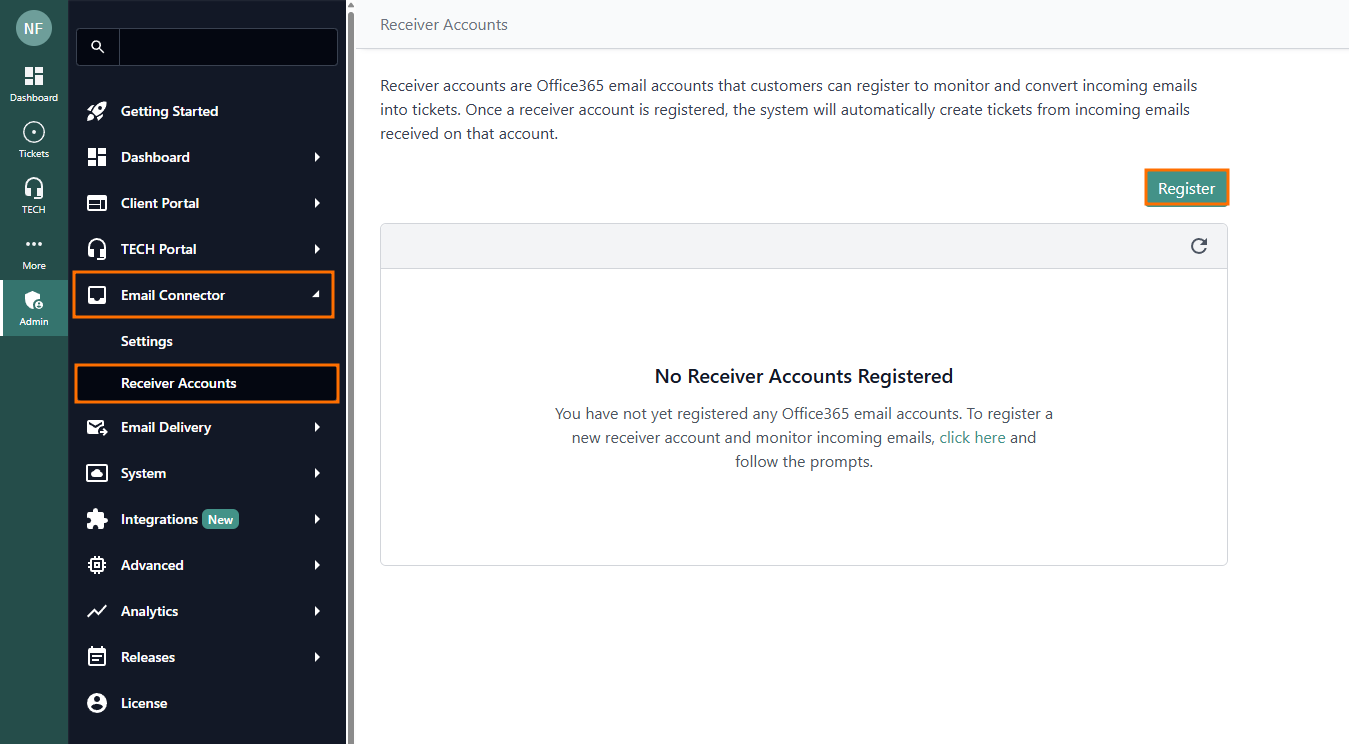
- In the dialog, enter the primary support email address
 This should be a dedicated support account, not your personal account
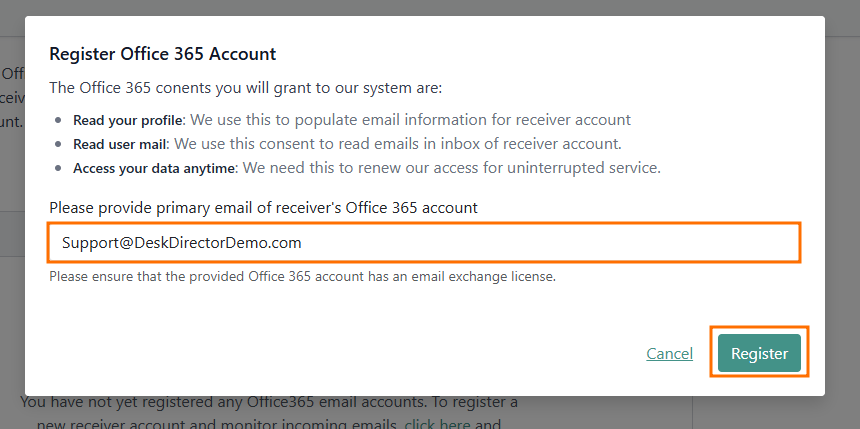
This should be a dedicated support account, not your personal account - Click Register to be redirected to the Office 365 consent page. Grant permission for Tokity to access and read emails from this account using the Microsoft Graph API
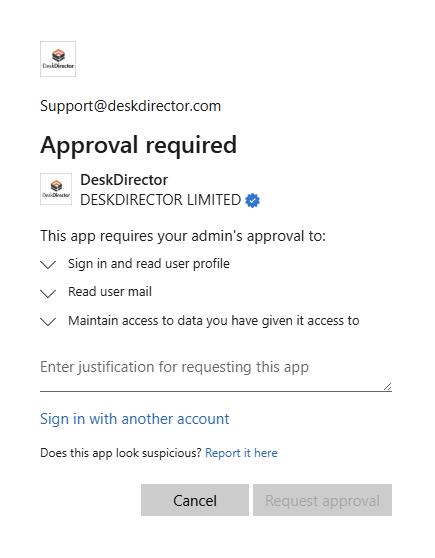
- Account Linking: Once consent is given, your account will be linked. The Email Connector will start syncing emails from the inbox and convert them into tickets or ticket comments
Managing Linked Accounts
After linking an account, you can view and manage its settings. The management interface contains several sections:
Info
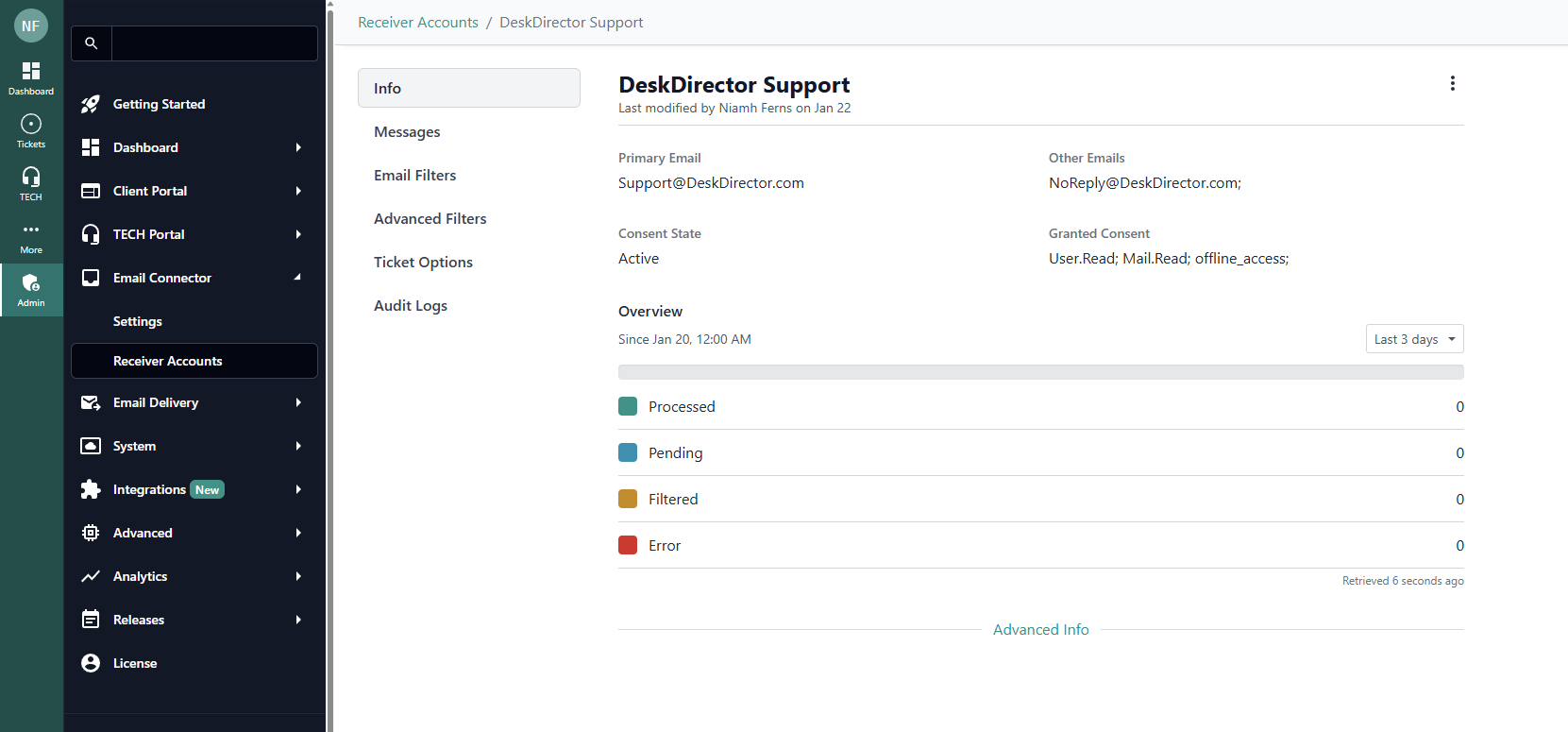
- Summary: Shows the linked account’s primary email and consent status (active or error)
- Consent Details: Lists the permissions granted through Office 365 Graph API
- Overview: Displays statistics, including the number of tickets processed in the last three days, pending tickets, filtered emails, and errors
Messages
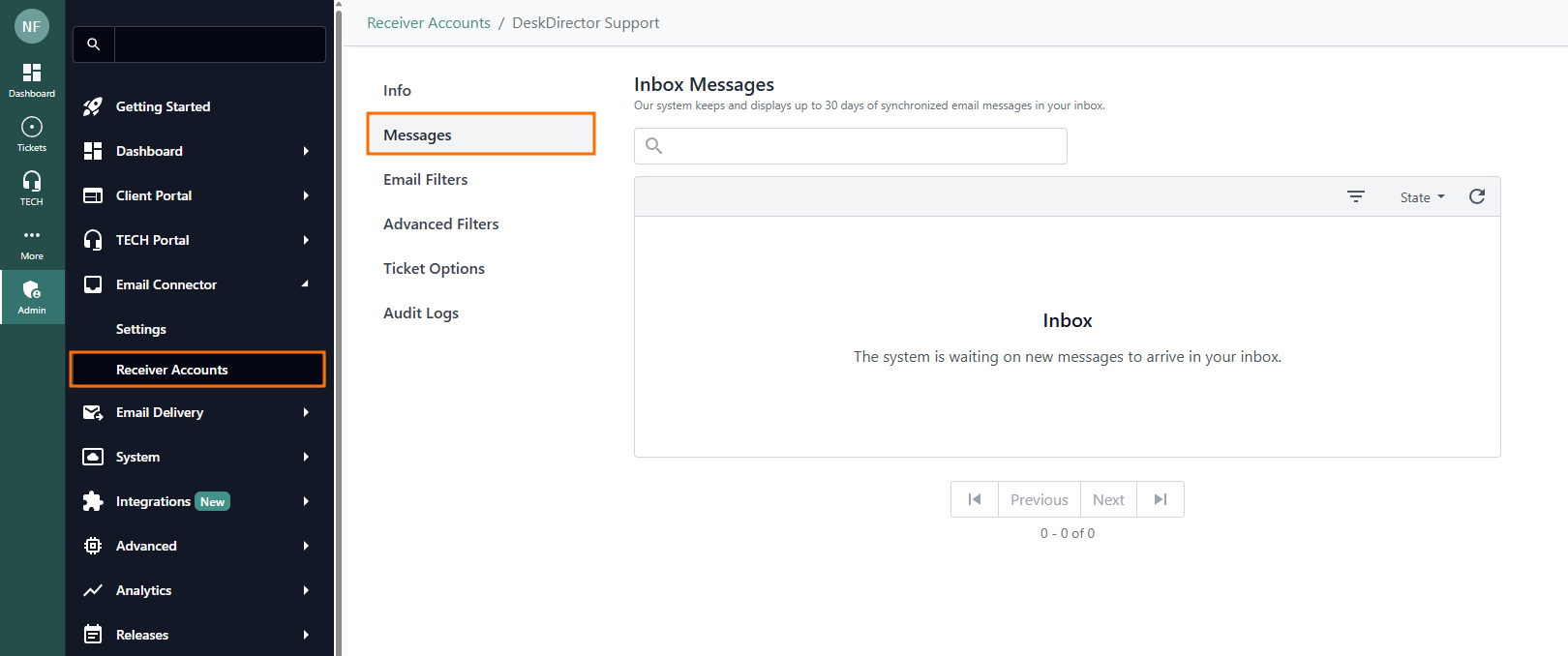
- Synced Emails: Shows all emails synchronised in the past 30 days
- Processing Status: Lets you check each email’s processing state, including whether it was converted to a ticket or comment, and helps diagnose any issues
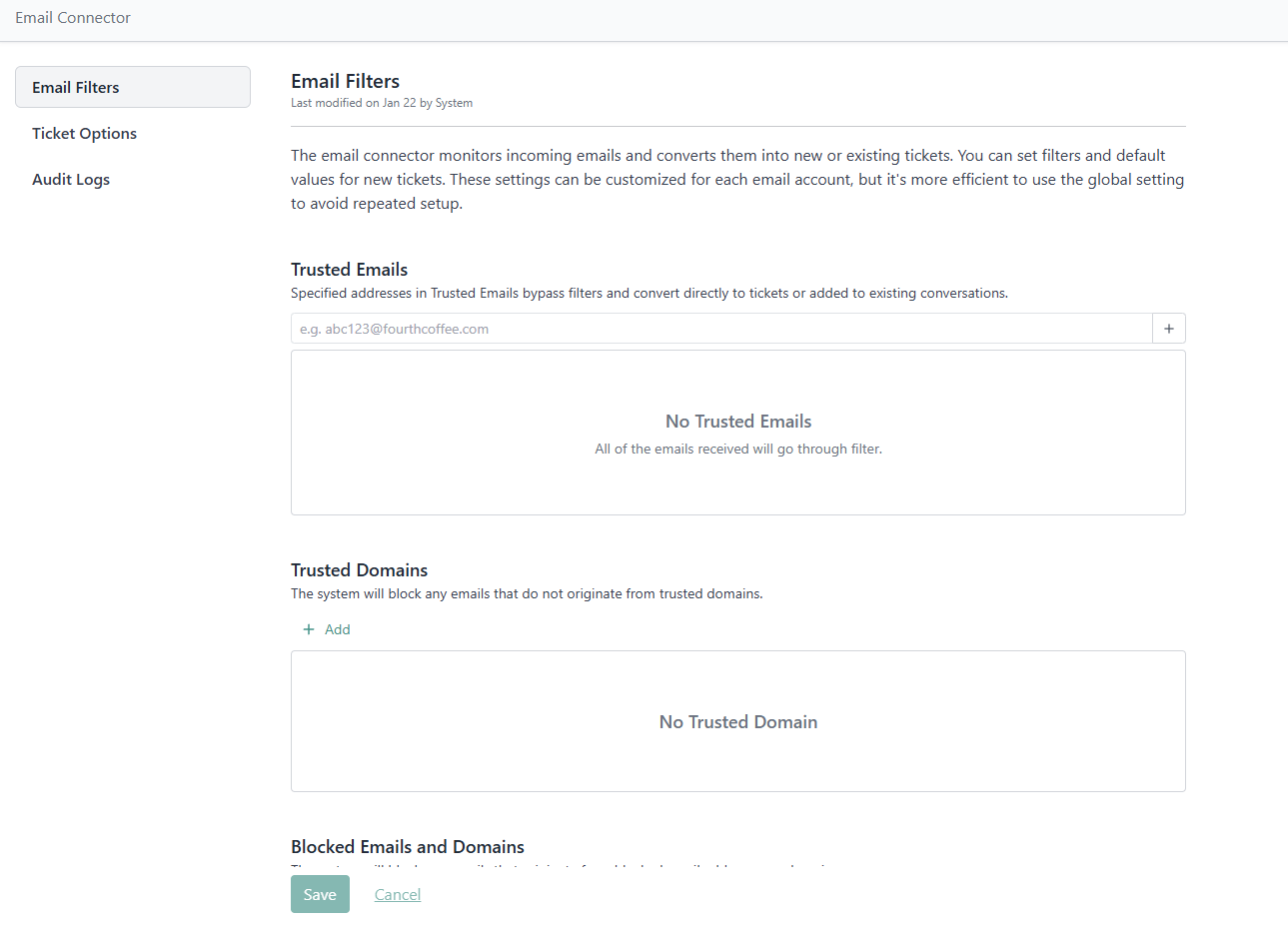
Email Filters
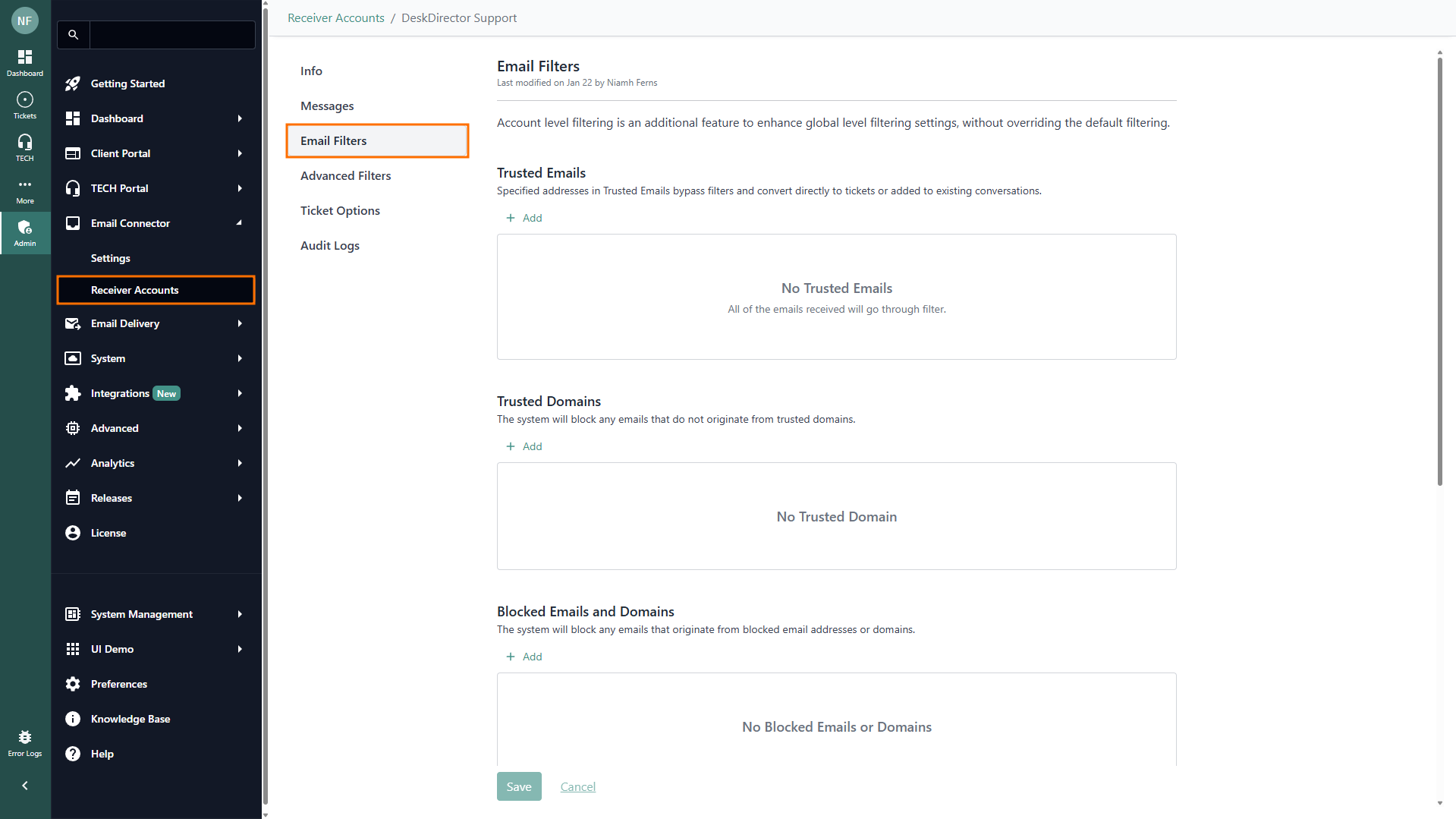
Configure how incoming emails are handled with these filters:
Trusted Emails: Emails entered here are always allowed. They bypass all other filters and are directly converted to tickets or added to current conversations. This overrides other settings. For example, if personal emails are blocked in advanced filters, you can whitelist a specific address here.
Trusted Domains: If you specify trusted domains, only emails from these domains can create tickets or comments. Emails from other domains will be ignored. Leave this list empty to rely on other filters
Blocked Emails and Domains: Any email address or domain listed here will be blocked and filtered out, preventing ticket or comment creation
Blocked Actions: Some system-generated emails start their subject with an action word followed by a colon (e.g., "Auto-Reply:"). Add these action words here to block those emails
Custom Block Rules: Create advanced block rules using regular expressions (regex) to filter emails based on sender address or subject
Advanced Filters
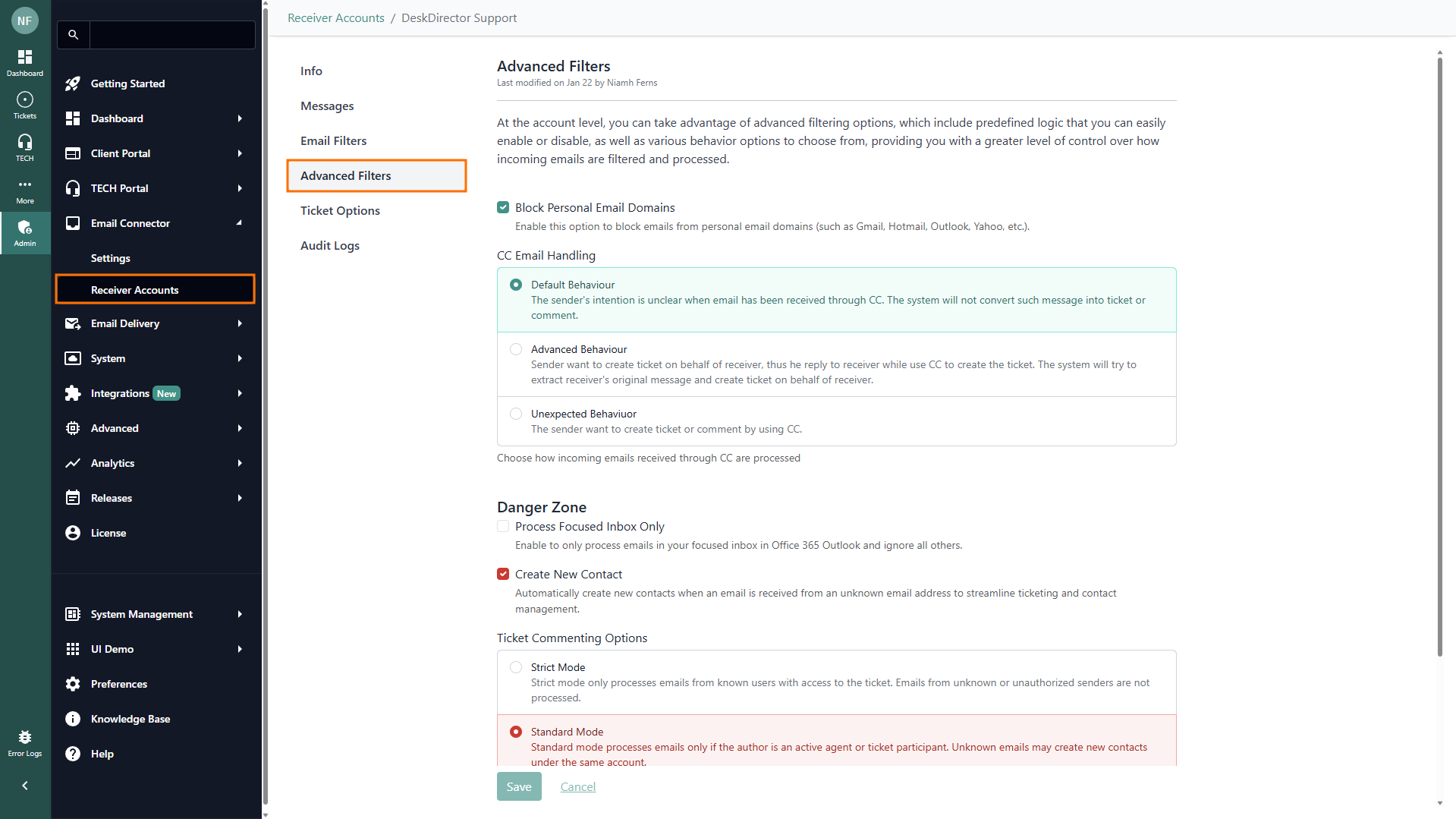
- Block Personal Email Domains: Toggle (default ON). When enabled, blocks emails from personal domains like Gmail, Hotmail, Outlook, Yahoo, and similar services.
- CC Email Handling: Choose how the system handles emails sent through CC:
- Default Behaviour: The sender's intention is unclear when the email is received through CC. The system will not create a ticket or comment from such messages.
- Advanced Behaviour: Sometimes, the sender wants to create a ticket on behalf of the recipient by replying to them and CC'ing the support email. The system will try to extract the original message and create a ticket for the intended recipient.
- Unexpected Behaviour: Any email where the support address is CC'd (not in the "To" field) will create a ticket or comment.
- Process Focused Inbox Only: When enabled, only emails in your Focused Inbox in Office 365 Outlook are processed, and other emails are ignored.
- Create New Contact: Automatically creates new contacts when emails are received from unknown addresses to streamline ticketing and contact management. (On by default.)
- Ticket Commenting Options:
- Strict Mode: Only processes emails from known users who have access to the ticket. Emails from unknown or unauthorised senders are ignored.
- Standard Mode: Processes emails if the sender is an active agent or ticket participant. Unknown emails may result in new contacts under the same account.
- Relax Mode: Processes emails from active senders and creates new contacts for unknown emails, regardless of account restrictions.
Ticket Options
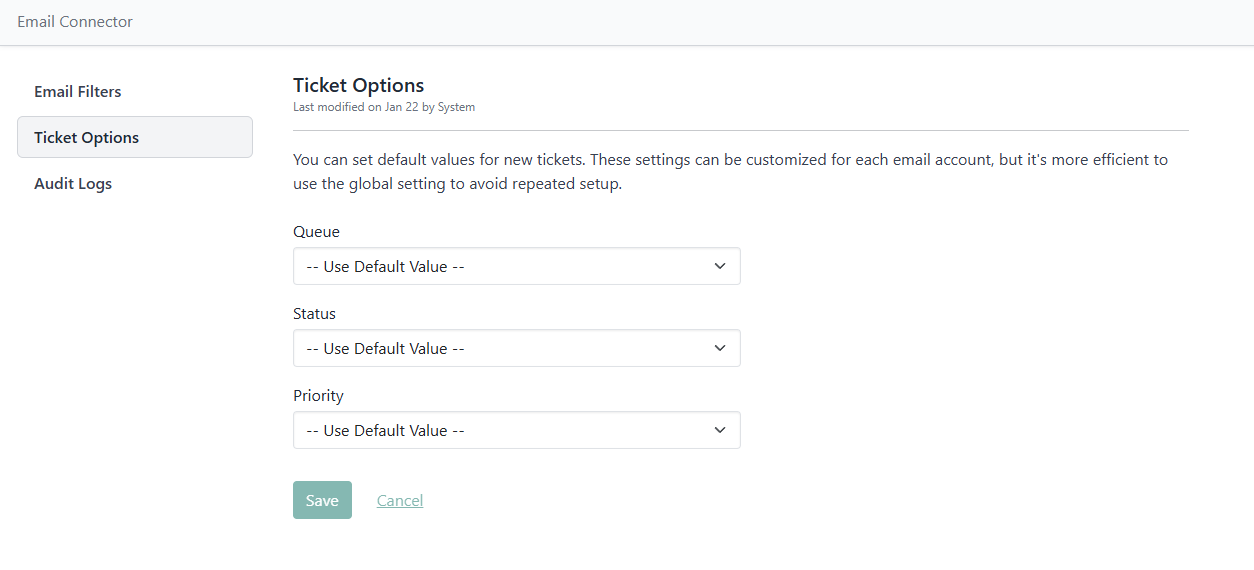
Ticket Routing: Set which queue, status, or priority new tickets should have when generated from incoming emails.
Audit Logs
Change History: View a log of who registered or modified settings for each linked account, ensuring traceability for all actions.
Important Notes
- Only emails in the linked account's inbox are processed
- Synchronised email records are kept for 30 days
- Ensure that the support account has the necessary Exchange license and is used only for support, not personal correspondence
Email Filtering with the Email Connector
In this article, we’ll explore how the Toki Iti Email Connector uses advanced filtering to ensure only relevant emails become tickets or ticket notes. By understanding how these filters work, you can better control the quality of your support tickets and avoid clutter with unrelated messages.
Key Technical Concepts
Before diving into the filtering process, let's review some important technical terms related to email processing:
- Email Subdomain and Domain: An email address consists of a subdomain (before the
@) and a domain (after the@).For example, inuser@example.com,useris the subdomain, andexample.comis the domain. - Email Header: The header contains metadata about an email, such as who sent it, delivery details, and whether it was automatically generated. Automatic delivery can be identified by header fields like
Auto-Submitted,X-Autoreply, orList-Unsubscribe. - Email Action Prefix: We refer to an "email action" as a specific prefix in the subject line, such as
Automatic reply:orUndeliverable:. These indicate common system-generated messages. - Personal Email Domains: Personal email addresses are those belonging to widely-used services like Gmail, Yahoo, Outlook, Hotmail, or Live. We use a prefixs like
yahoo.,outlook.,hotmail., andlive.to block personal emails across regions. This list is updated regularly, and users are encouraged to suggest additions. - Known Automatic Email Deliverers: These are summarised lists of automatic email delivery addresses, mostly from Microsoft and other major services (e.g.,
o365mc@microsoft.com,azure-noreply@microsoft.com,do-not-reply@stackoverflow.email). We continually update this list based on user input. - No-Reply Email Addresses: These are email addresses meant for sending only, not receiving. We currently exclude emails where the local part is
no-reply,noreply, ordo-not-reply. Users can suggest other patterns to expand this list.
How the Email Connector Filters Emails
The Email Connector checks incoming messages using the following sequence of filters.
Filtering Sequence
- Ensure Sender Exists
This is a defensive check to verify that the email message includes sender information. Occasionally, malformed emails—such as those generated incorrectly in Office365 Outlook—may have a missing or null sender (the "From" field). While almost all emails should have a sender, this step ensures that any email without sender details is excluded from processing. - Trusted Email Check
If the sender is listed as a trusted email at either the global or account level, the message bypasses all other filters. - Automatic Message Header Check
The system checks the email’s header for fields likeAuto-Submitted,Autoresponder,X-Autoreply, orList-Unsubscribeto identify auto-generated messages. - Known Automatic Deliverer Check
Emails from known automatic delivery addresses (e.g., Microsoft notifications) are filtered out. - Action Prefix in Subject
If the subject line starts with a known action prefix (e.g.,Automatic reply:,Undeliverable:), the message is blocked. - No-Reply Email Address Check
Messages from senders with local parts likeno-reply,noreply, ordo-not-replyare excluded. - Self-Sent Email Check
Emails sent from the support account to itself (e.g.,support@yourdomain.comsending tosupport@yourdomain.com) are filtered out. - Deliverer Email Check
Emails sent from addresses used by your system for ticket updates, login tokens, or broadcasts are excluded. - Block Personal Domains (Optional)
If enabled, emails from personal domains likeoutlook.com,gmail.com,yahoo.com,aol.com, etc., are blocked. - Focused Inbox Only (Optional)
If enabled, only emails in your Focused Inbox in Office 365 are processed. - Ignore CC Behaviour (Optional)
If enabled, emails received via CC are ignored. - Blocked Emails
Emails from addresses blocked at the global or account level are excluded. - Blocked Domains
Emails from domains blocked at the global or account level are excluded. - Trusted Domains Only (Optional)
If trusted domains are defined, only emails from these domains are processed; all others are ignored. - User-Specified Action Prefix
Filters out emails with subject lines starting with user-specified action prefixes, including multilingual options. - Custom Regex Filter
Applies user-defined regular expressions to block emails based on subject or sender address. - Spam and Loop Prevention
To prevent spam and email loops, the system checks if the sender’s email address has sent more than 20 messages in the last hour. If this threshold is exceeded, further emails from that sender are ignored for the rest of the hour. This helps block spammers and prevents email loops, which can occur when two ticketing systems automatically reply to each other, especially if one system does not include automatic email headers.
